The UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has rolled out its latest report detailing the supervision of algothmic trading. The in-depth report delves into both good and bad practices in a series of cross-firm reviews, touching on key areas of emphasis.
Discover credible partners and premium clients at China’s leading finance event!
[gptAdvertisement]
The introduction of automated technology into the financial services space has mostly been a positive force. Largely seen as a displacement or improvement on traditional technology or trading systems, algos have helped abruptly increase Execution speeds while at the same time reducing costs.
Automated trading does remain as a double-edged sword however, as algos and other techniques do foster certain amounts of risks. For example, in the absence of appropriate systems and controls, the increased speed and complexity of financial markets can potentially turn normal manageable errors into extreme events with potentially wide-reaching implications.
Consequently, the FCA has compiled a study and analysis to explore this area as it has gained a stronger focus as of late. The FCA and others are looking to keep pace with a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Megan Butler, Director of Supervision, Investment, Wholesale at the FCA, commented on the report: 'This report is relevant for all firms developing and using algorithmic trading strategies in wholesale markets. Firms should consider and act on its content in the context of good practice for their business.”

Bloomberg
In particular, the report focused on five specific areas within algo trading compliance as it pertains to markets. This includes defining algo trading, the development and testing process associated with this trading, suitable risk controls, government and oversight protocols, and market conduct.
The report includes a detailed assessment of the development and implementation procedures used by firms for algorithmic trading. Moreover, the entire development, testing and deployment lifecycle was examined, and further analyzed via interviews with front line staff such as traders, quantitative researchers and software developers.
First and foremost, the report revealed a generally positive sentiment regarding the appropriate implementation of measures needed to reduce potential risks in algo trading. However, there is certainly latitude for improvement in a number of areas.
For example, a number of firms lacked a suitable process to identify algorithmic trading across their business, while some venues did not adequately have appropriate documentation in place to demonstrate suitable development and testing procedures.
Furthermore, several films need to do more to identify and reduce potential conduct risks fostered by their algo trading strategies. One way to remedy this would be to conduct market abuse training for staff involved in the development and implementation processes.
How does one define algo trading?
The FCA sought to establish an appropriate process to identify algo trading, while also managing ‘material changes’ and maintaining a unified inventory of algo trading across the business. Of note, in order to comply with the requirements of the now implemented MIFID II laws, firms need to develop processes to identify algo trading.
Overall, the FCA struggled to pinpoint the exact definition and scope of algo trading as it can vary depending on the type of firm and strategies deployed. That being said, algo trading strategies can be classified as either investment decision or execution algorithms. It
is important to distinguish that some firms combine investment decision and execution algorithms into a single algo trading strategy.
The FCA suggested extensive reviews, whilst consulting all relevant business aspects to consider at length how trading algos are used within a given firm. Good practices would entail these firms being able to develop appropriate definitions and ensure relevant activities across the whole business are captured.
By extension, firms were advised not to apply a broad definition, without consideration of the types of activity undertaken as it will not properly capture the extent of algo usage.
Development and testing
The FCA also focused on ensuring firms maintain proper, consistent, and well understood development and testing processes. These were deemed a necessary construct in which to identify potential issues across trading algos prior to full deployment.
The report cites suggests that firms who maintain a robust development and testing process supported by the appointment of a project lead with responsibility to oversee the entire development and testing process. Additionally, good practices include breaking down the development process into separate phases in which to establish independent checks and balances at each stage.
Firms are cautioned against exercising any inconsistency in testing. For example, different trading desks or business lines use different methodologies.
Risk controls
One of the most important areas the report looked into were the deployment of risk controls. All firms are encouraged to maintain appropriate risk controls to protect their own interests, and most importantly, those of their clients:
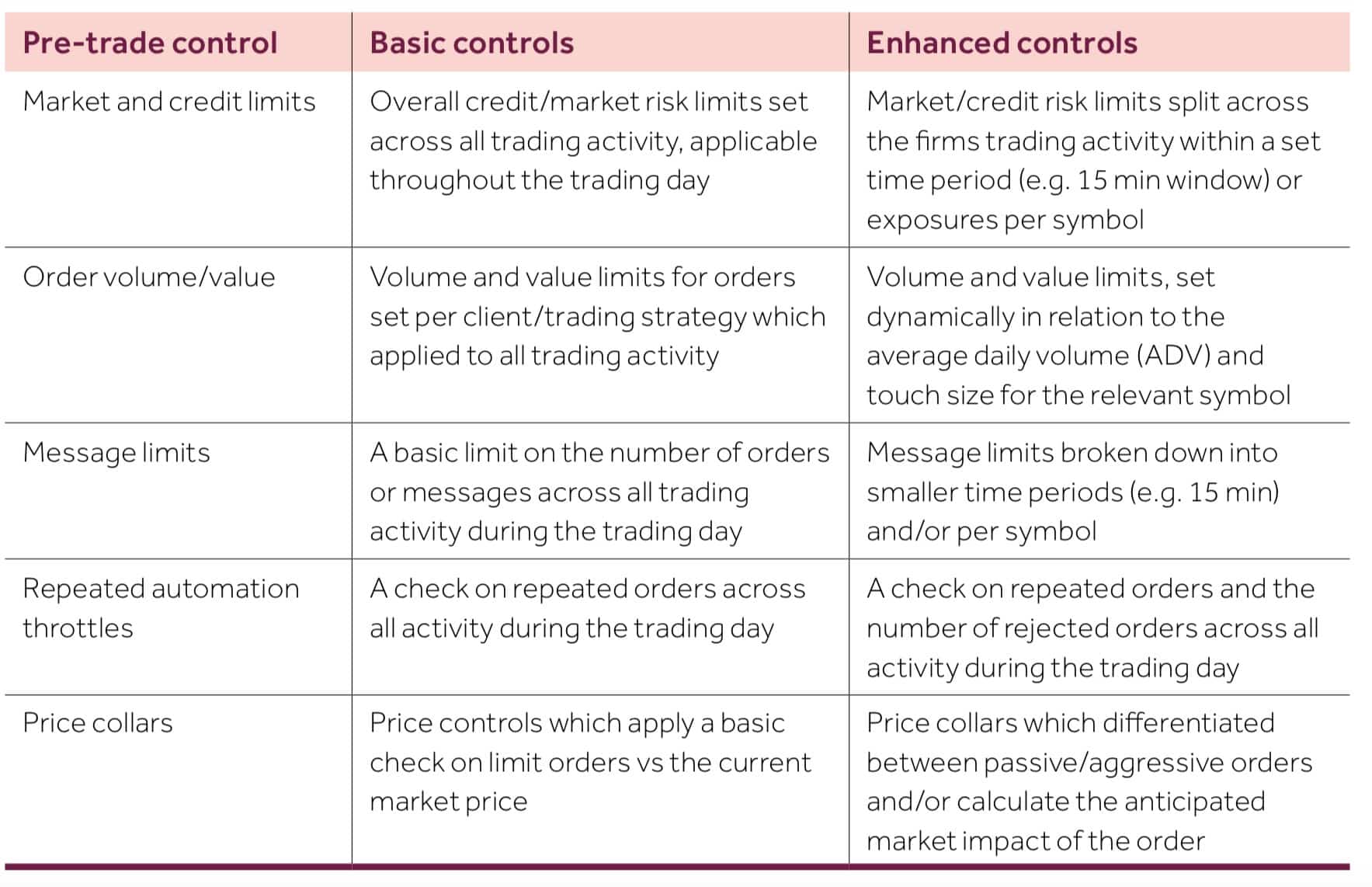
Source: FCA report on Algorithmic Trading Compliance in Wholesale Markets
Governance and oversight
Oversight proved to be a key area that the report repeatedly cited. A strong governance framework was therefore identified as a corollary for effective Risk Management , while also being fundamental in reducing the risks associated with algorithmic trading strategies.
Overall, the report found that sound governance framework supports a robust development, testing and deployment process, complete with independent validation procedures, suitable risk management controls, and appropriate monitoring and surveillance.
Market conduct
Finally, the review looked into the role that algo trading plays across financial markets. It is therefore instrumental that firms consider the market conduct implications of their trading activity as it does in the aggregate influence the overall market integrity.
Firms were cautioned against adhering to basic market abuse alerts such as insider dealing or layering and spoofing. Rather, it is important to investigate for all types of market manipulation, which can be associated with algorithmic trading. This includes momentum ignition, quote stuffing and reference price gaming.






















