Bitcoin is the world’s leading cryptocurrency, and even those unfamiliar with the crypto and Blockchain world would have heard of it in some capacity.
For some, it is the future of finance; for others, it is a volatile fad too closely associated with criminal activity on the dark web. Those that are curious about acquiring bitcoin, however, can have a difficult time understanding the practical aspects of sending and receiving Bitcoin. That's what we'll cover in this article.
Before Making Your First Transaction
It is important first to consider the length of time a Bitcoin transaction tends to take, which may vary far more than a bank transfer.
Two primary variables affect the transaction time for Bitcoin. The first is the amount of activity going on in the network.
Ultimately, if there is high network density (meaning that there are a lot of transactions to process), the transaction time will be far longer. The Bitcoin network processes an average of 3-4 transactions per second; if there are tens of thousands of transactions in the queue, it's going to take a long time.
Miners need to process each block, and it takes time for them to do that. If transaction fees are higher, however, miners are more likely to process the transaction quicker. Due to the volatile nature of the network, this means transactions can take anywhere from a few minutes to more than 12 hours to process, depending on network conditions.

Bloomberg
How do Bitcoin Transactions Work?
If someone wants to send bitcoin, their intention is logged when they commence the transaction. Then, the nodes scan the whole bitcoin network to confirm that the bitcoin is there to send and that it hasn’t already been sent to someone else.

Once this information is verified, the transaction gets included in a "block" which is attached to the previous block - hence the name: blockchain. Transactions cannot be canceled or manipulated, because this would mean altering all the blocks that came after, a virtually impossible task.
The bitcoin wallet does not hold bitcoin. Instead, it does is holds the bitcoin's private key and public address. This 'public address' - a long string of 34 letters and numbers - is also referred to as the "public key." Private keys are strings of characters that control coins--this is what is stored in a crypto wallet. The signature from the private key is what validates the transaction and allows it to go through.

How to Send a Bitcoin Transaction
To send Bitcoin, you need to begin by getting a Bitcoin wallet. We’ll use Coinbase to illustrate as it is one of the most popular sites for these types of transactions.
As mentioned, there are two key factors to consider when making a Bitcoin transaction. You need a private key and a public address to send the coins to. Coinbase does, however, hold your private key, so it is not entirely within your control.
This is just something to consider from a security perspective; if you find Coinbase to be a trustworthy entity, then allowing them to keep your private keys in storage shouldn't be an issue. If this is a problem, however, you may want to consider storing your crypto in a way that allows you to have total control over your private keys.
Steps for Sending Funds:
Step 1: Open your software wallet and press the "Send" tab, or use the "Trade|Send Bitcoin" which can be found on your wallet menu.
Step 2: Enter the destination address for your recipient's wallet. This is the public address, add it by copy and pasting it, QR code, or writing it out by hand.
Step 3: Select a label to track your transaction.
Step 4: Enter the amount you’d like transferred in the BTC box.
Step 5: Review the details and make sure the info you entered is correct, as the transaction cannot be reversed.
Step 6: Press "Send" to finalize the transfer.
How to Receive Bitcoin
To receive Bitcoin, you only need your wallet and your public address (as well as your security features to access the wallet obviously).
Step 1: Once you’ve set up your Coinbase account, click the “Accounts” tab. Here and you will find your wallets. Click the “Receive” button on your Bitcoin wallet.
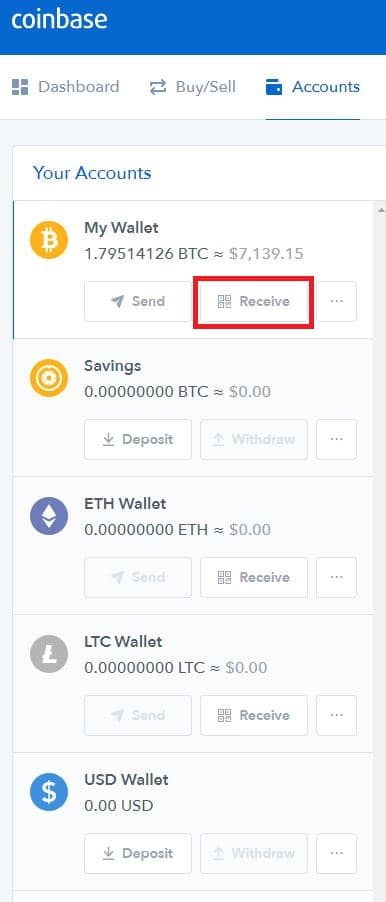
Step 2: The address for your Bitcoin will be displayed. Share this address with anyone who would like to send you Bitcoin.
If using an exchange to obtain Bitcoin, you will need to pay for the Bitcoin, which can be done via Paypal, Bank Transfer or cash depending on what you and the trader agree to.
Are Bitcoin Transactions Anonymous?
The common assumption is that Bitcoin transactions offer complete anonymity in a way that bank transfers and cash Payments do not. This is not strictly true, however, as an increasing number of web merchants leak transaction details about purchases, allowing your coins to be traced back to you. While privacy is offered, using these transactions is sort of like writing under a pseudonym. If someone can trace one of your transactions, all of them become traceable.
This occurs due to web trackers and cookies which are pieces of code that track the way sites are used and passed on to third parties. This info can be sent to Google, Facebook, etc. so they can analyze trends. In the same way, governments, law enforcement agencies, and hackers can just as easily gain access to this information.
For this to occur, an eavesdropper or a leaker is required. However, according to a study by Goldfeder, 53/140 Bitcoin merchants have leaked info to a vast number of third parties. This is primarily done for adverts and analytics but is still something to be aware of.






















