An ‘alt-season’ occurs when a number of altcoins quickly and astronomically rise against both the dollar and Bitcoin at once.
Perhaps the an alt-season occurred was in the fourth quarter of 2017, when a number of altcoins suddenly “mooned” and continued on an upward trajectory: even though Bitcoin was also astronomically increasing in price, a number of altcoins were performing even better, and continued to perform well eleven after the price of Bitcoin began to slump in mid-December of that year.
There certainly have been plenty of recent examples of altcoins performing fantastically well: LINK (Chainlink) has skyrocketed from $4.08 to $8.34 over the course of the last month, a whopping 104.4 percent increase; ADA (Cardano) increased by 51.89 percent ($0.079 to $0.12) over the course of the last month (at press time).
Similarly, XTZ (Tezos) rose from $2.64 to $3.11 (a 17.8 increase) over the last month; DOGE (Dogecoin) rose from $0.002 to $0.0029, a 45 percent increase over the same time period (though it went as high as $0.0048 at one point over the course of the month. XLM (Stellar Lumens) soared from $0.072 to $0.10.
Are we entering into another alt-season? What does this mean for Bitcoin--and for cryptocurrency markets more generally?
Bitcoin’s stagnancy could be contributing to an altcoin surge
A number of analysts have noted that alt-seasons typically tend to occur after long periods of stagnation in cryptocurrency markets--particularly, in the Bitcoin market.
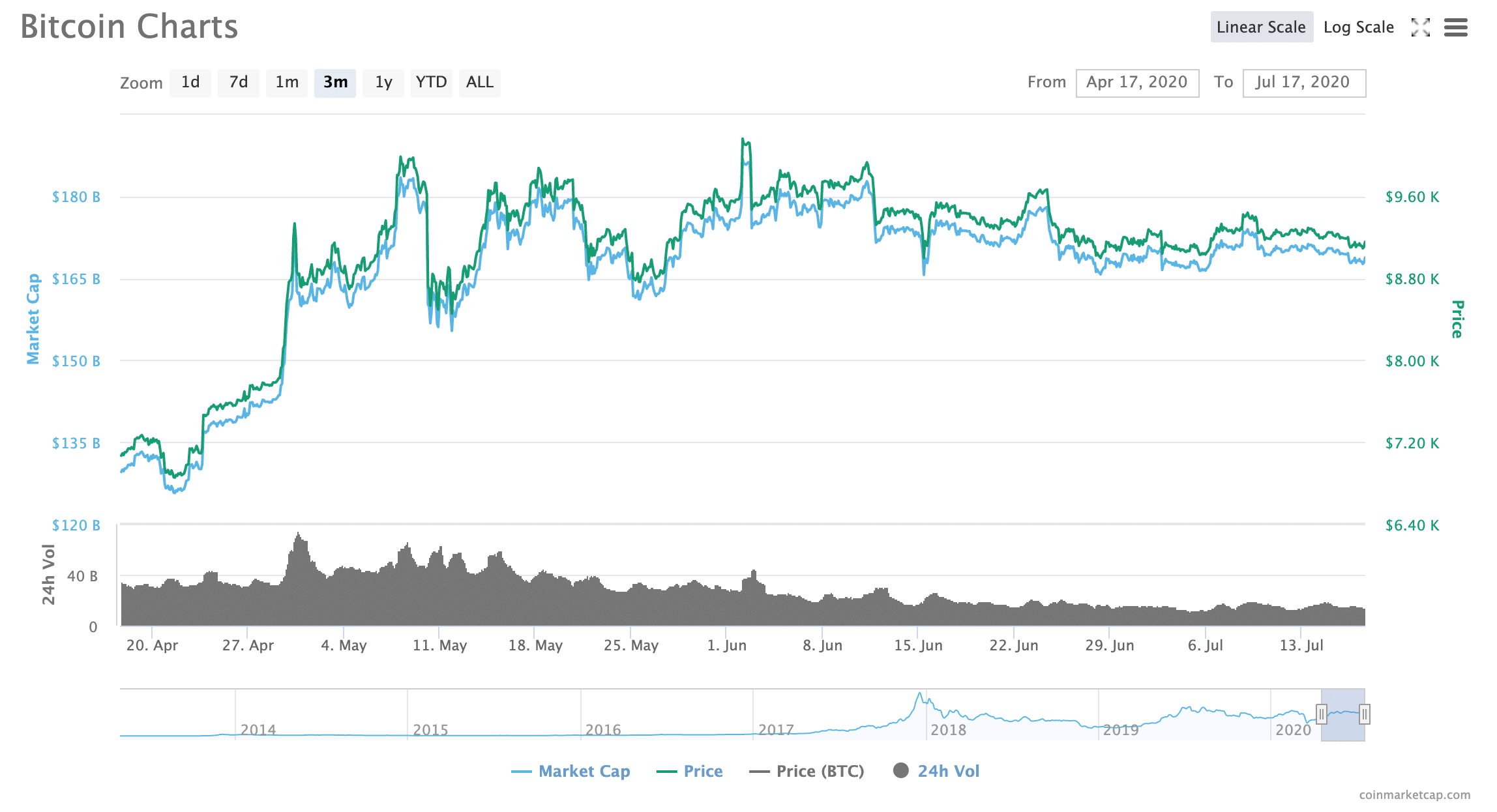
Stagnation has certainly been the trend for Bitcoin, which has hovered between roughly $9,000 and $10,000 for approximately two months.
David Waslen, chief executive and founder of HedgeTrade, explained to Finance Magnates last week that some of the recent action in altcoin markets may be a sort of run-off effect from Bitcoin traders--who, traditionally speaking, “love volatility”.

David Waslen, chief executive and founder of HedgeTrade.
“To be able to profit off an asset class that can move 10% in a matter of minutes provides opportunities that you’re unable to find in a lot of the traditional asset classes,” Waslen explained. “Superior traders have been able to lock massive returns in the past.”
However, as Bitcoin has become less and less volatile, traders have sought to get their volatility fix elsewhere: “with the drop in volatility you’ve seen a drop in [trading] volume as traders are hesitant to take positions, as there are fewer opportunities.”
And Bitcoin’s dominance is slipping as altcoins seem to be gaining more popularity among traders: "Bitcoin's market dominance has been in decline since early May 2020,” Simon Peters, market analyst and crypto expert at eToro, said to Finance Magnates.
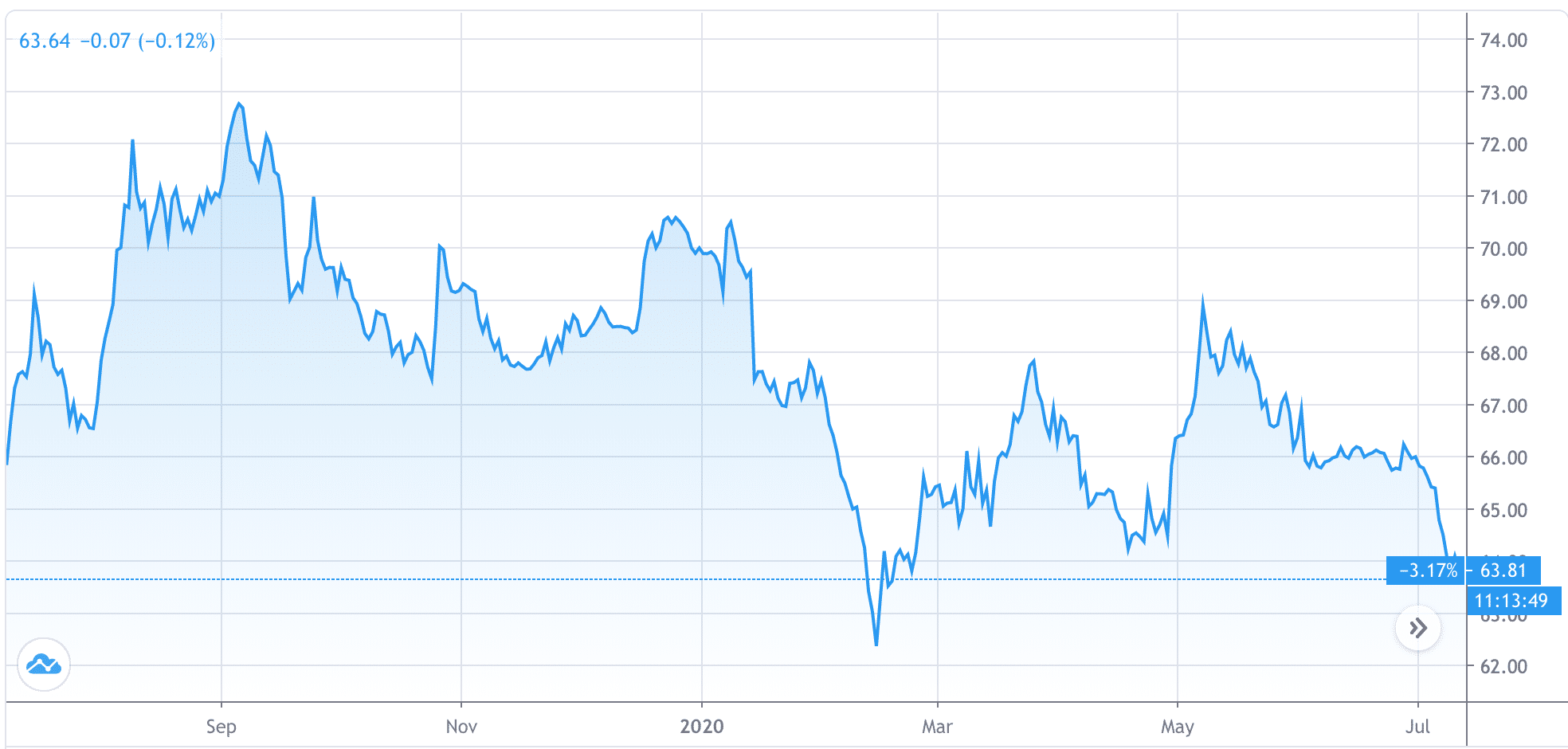
Bitcoin Dominance Index, via TradingView.
However, Peters doesn’t necessarily believe that the positive performance of certain altcoins constitutes an alt-season--at least, not yet: “at this point I would be more inclined to say we are in 'alt season', if [Bitcoin dominance] falls below 60%, mirroring what happened the last time we had a real alt season in late 2017 to early 2018,” he said.
At press time, Bitcoin dominance sat at roughly 63 percent.
”Multiple contributing factors that have led altcoin markets to surge”
Bitcoin’s lack of volatility isn’t the only reason that some altcoins may be performing so well.
“There are multiple contributing factors that have led altcoin markets to surge,” Waslen explained.
And the reasons behind each coin’s individual surge may be unique: for example, “we’re recently seen $DOGE spike when getting pumped by influencers on TikTok,” he said.
Simon Peters also told Finance Magnates "ADA's recent gains are most likely because of the Shelley upgrade, being implemented at the end of July to the Cardano mainnet,” and that “it could be that investors who wish to benefit from staking going forward are buying now in preparation.”
“Similarly, there has been an uplift in Tezos investment now that more crypto exchanges and platforms are starting to offer XTZ rewards,” Peters added.

Simon Peters, market analyst and crypto expert at eToro.
Additionally, "LINK has been gaining in value after some bullish news around Chainlink partnering with various projects in the DeFi space. One key partnership is with China's Blockchain Services Network, which will allow real-world data to be used by the applications being built on the Chinese BSN blockchain infrastructure.”
David Waslen also commented that the LINK surge--and possibly other altcoin surges--may be feeding itself: “last week, LINK posted a new all-time high which can sometimes lead to people FOMOing in,” he said. In other words, as some of these coins experience organic rises in price, speculative investors may see an opportunity to profit off of the bullish movements.
DeFi tokens may be in the spotlight at the moment
There also seems to have been a concentration in upward price movements in coins that are associated with DeFi platforms.
For example, COMP, the native token of Compound’s lending platform, famously surged to roughly $360 about two weeks after its launch in June; while the price has since corrected to the $150-$170 range, the coin appears to be holding fairly steady.
David Waslen explained that the popularity of these DeFi assets may be due in part to the increasingly popular practice of “yield farming”, which--by various mechanism--allows people to earn fixed or variable interest by investing crypto in the DeFi market; the most common example of this seems to be interest-bearing crypto accounts.
Will McCormick, director of communications at global cryptocurrency exchange OKCoin, also explained to Finance Magnates that “the process of earning staking rewards in the form of tokens and/or interest in return for providing Liquidity to a DeFi protocol,” has indeed drawn a lot of new users and holders to DeFi tokens.

Will McCormick, director of communications at global cryptocurrency exchange OKCoin.
“In the last month we have seen the dollar value of assets locked in DeFi apps more than double, and almost 5X in the last 12 months. The DeFi ecosystem is finding the right incentive structures to encourage participation in the DeFi networks, which will aid the next phase of innovation in the DeFi space to push the industry further.”
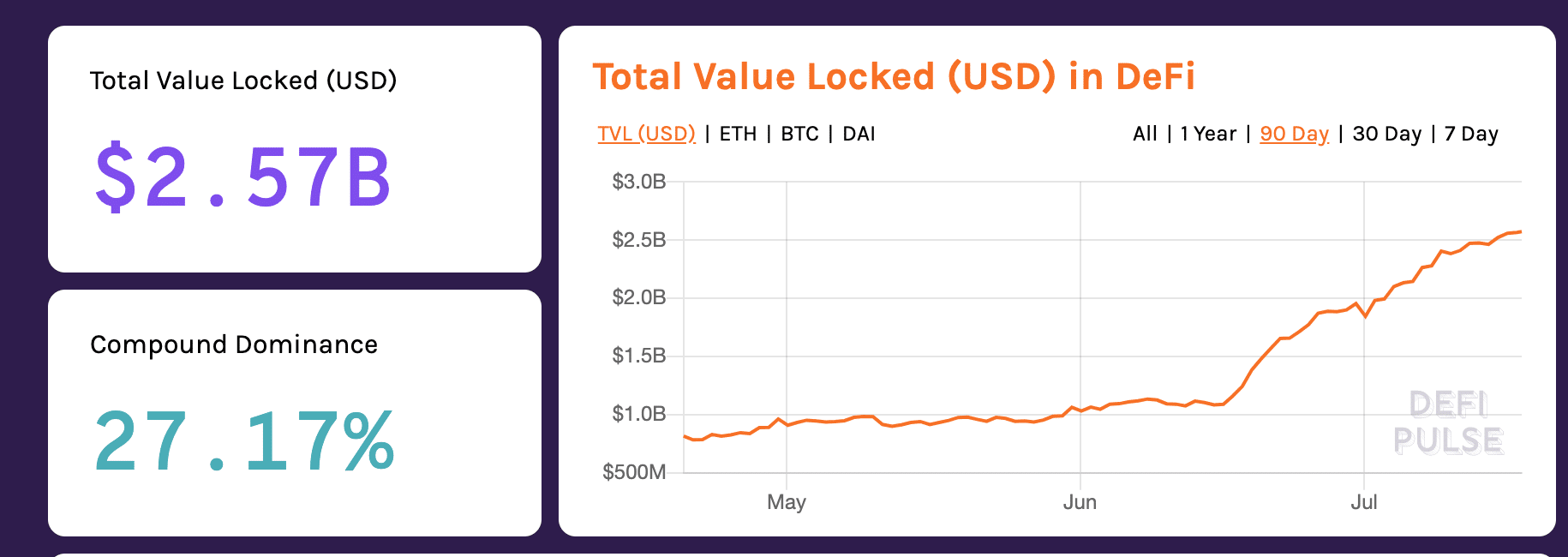
via DeFi Pulse
Indeed, “you’ve had the DeFi farming phase just now beginning, where people are finding ways to earn during times of deep economic strife, “ Waslen said.

Dave Parkinson, the chief operating officer of international media and publicity firm Lamourie Media.
Dave Parkinson, the chief operating officer of international media and publicity firm Lamourie Media, also told Finance Magnates that “platforms that participate in decentralized finance like Chainlink and Compound have been attracting attention from institutional investors.”
Additionally, “ADA's commitment to implementing DeFi applications on its blockchain are also attracting interest from the institutional side.”
And, of course, there has been some speculation that the DeFi space may be crypto’s new hype machine: “ DeFi or Decentralized Finance has become the crypto space's new ‘flavour of the month; just as ICO's were back in 2017,” Dave Parkinson said.
“With dozens of new emerging projects on the horizon I'm always keeping an eye open for the next hot up-and-comers,” he said. “I expect the DeFi space to remain hot throughout the rest of the year into 2021 with many of these new projects reaching the top 20 or higher by this time next year as the institutional money floods in.”
”Each of these tokens has its own fundamentals.”
Another possible contributing factor to the altcoin price surges is that people may simply be using altcoins more often than in the past.
“I think in general there are more people using altcoin blockchains during an altcoin price surge,” David Waslen told Finance Magnates. “Especially with those projects that have their token well integrated into their platform.”
Indeed, Andrea Zanon, chief executive of the Nimbus Platform, said that “each of these tokens has its own fundamentals.”

Andrea Zanon, chief executive of the Nimbus Platform.
“ADA is a generic blockchain platform, improving on the use case of Ethereum with built-in mechanisms to drive efficiency in operational capacity,” Andrea explained.
“The others are examples of emerging asset classes,” he continued. For example, “COMP is a decentralized finance platform, which automates and secures financial services on top of blockchain platforms”
Additionally, “LINK is an interoperability layer, making it possible to communicate between blockchains. In technical terms, the state of operation executed on one blockchain can be exported to another through an interoperability layer, such as LINK.”
What are your thoughts on the recent altcoin price surges? Let us know in the comments below.






















