Blockchain technology and its application in Cryptocurrencies have its fault-tolerant security rooted in the consensus mechanisms.
The consensus mechanism of a blockchain provides the necessary agreement on a single data value or a single state for that blockchain network.
The two most popular consensus mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of State (PoS). The Proof of Work consensus is the oldest consensus mechanism and it is used on the Bitcoin Blockchain.
Proof of Stake, (promoted by the Ethereum network) was developed to address some of the inherent risks in the PoW consensus mechanism.
Proof of Stake is built around the idea that that the number of block transactions that a person can validate or mine on a blockchain is directly proportional to the number of coins he or she holds.
This piece provides insight into how the value proposition of Proof of stake is gradually extending beyond mining into trading and investments as cryptocurrency investors continue to grapple with market volatility.
Cryptocurrencies are still in a bear hug, but longs can still profit
It is easy to place profitable cryptocurrency trades and investments during a bull market. It doesn’t require any special knowledge, effort, or experience to buy low and sell high.
The crypto bull run 2017 in which bitcoin outperformed other asset classes is a case in point on how everybody can easily become be an ‘expert’ trader and investor during an extended bull run.
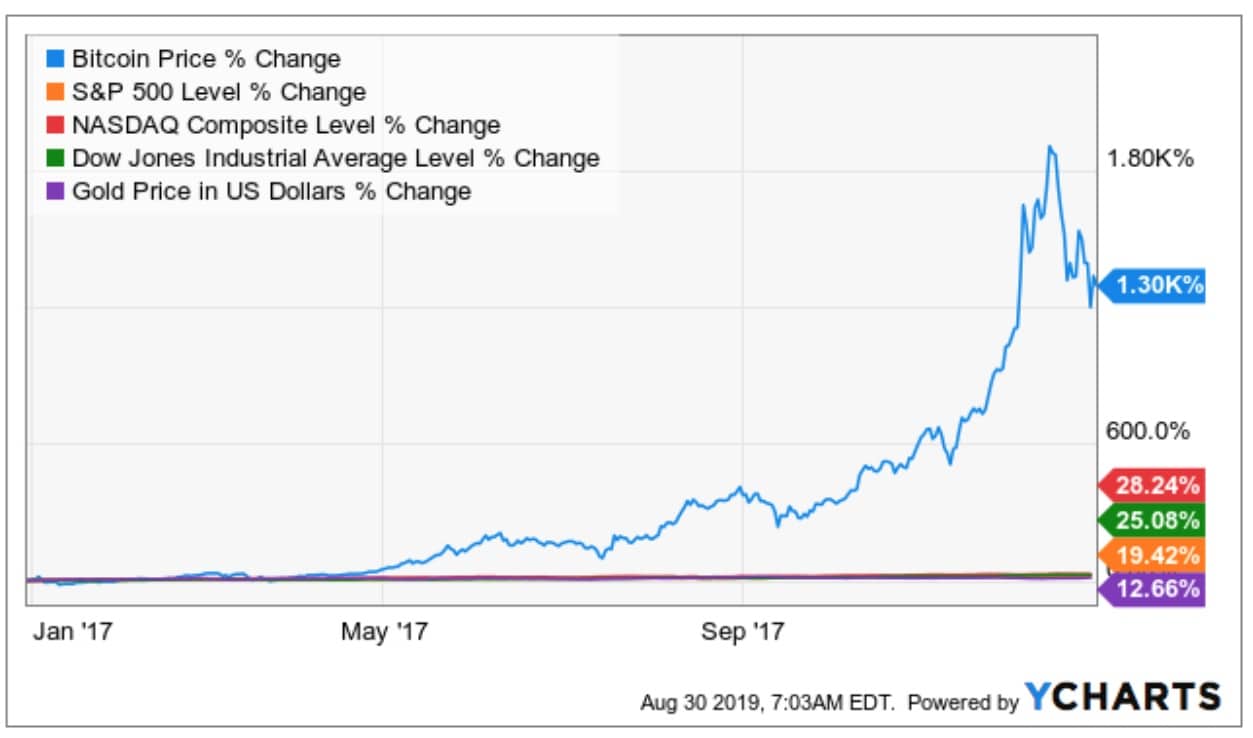
However, when cryptocurrencies find themselves in a bear market, traders tend to get burned, investors see a significant value of their portfolio being wiped out, and new money hesitates to enter the market.
The 2018 bear market is a good example of how fast the value of cryptocurrencies can be eroded relative to traditional assets during a bear market.
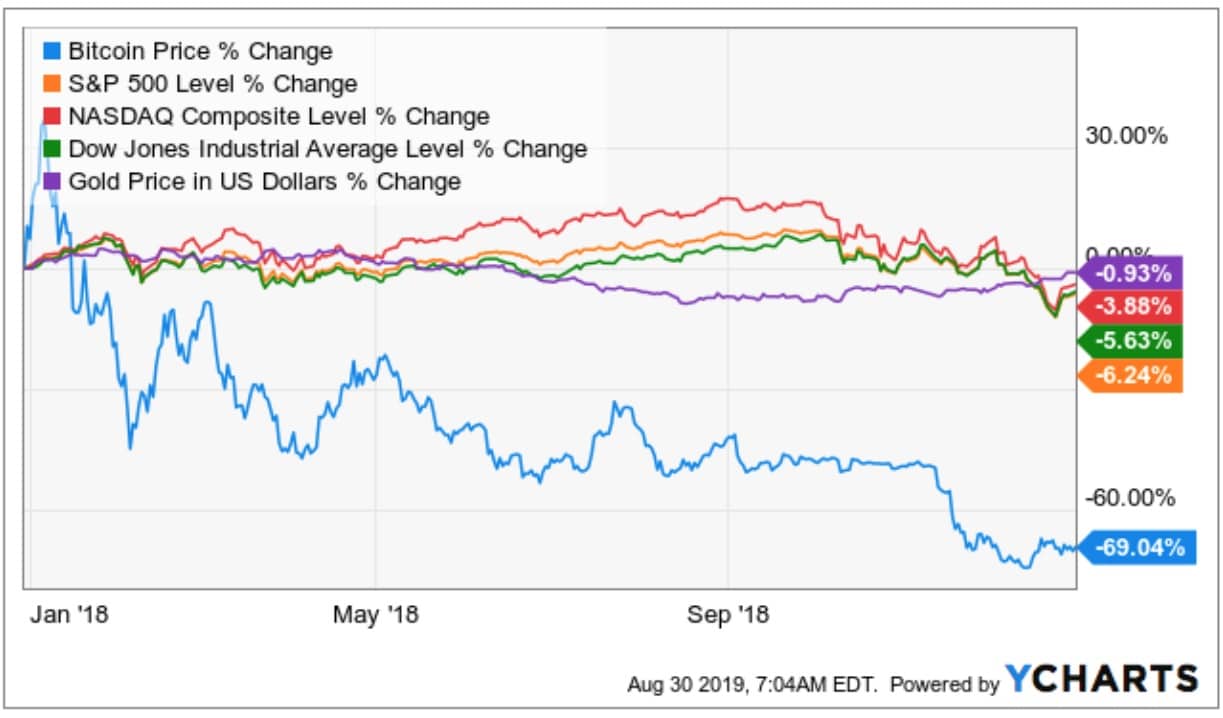
Interestingly, during a bear market, smart traders tend to take the shorting route and they might even add leverage/margin trading to increase their profits.
Unfortunately, long-term investors don’t seem to have any cards to play in a bear market.
Hence, many long-term hodlers are usually forced to stay put during a bear market in the hopes that the market will eventually return to bullish ways.
Introducing token staking
Staking your tokens on a PoS Blockchain involves locking up your crypto holdings as collateral for network resources to compete for and to add the next block to the chain.
Staking provides a financial incentive for people to provide the network resources for validating transactions and for maintaining the integrity of networks services.
Investors who stake their tokens typically earn rewards for staking in the cryptocurrency, market similar to the way people earn dividends and interest on stocks or bonds on Wall Street.
Long-term hodling investors typically leave their cryptocurrencies unused and unmoved in their wallets.
Hence, the fact that staking provides returns denominated in the asset being staked irrespective of market conditions makes it a better way to maintain a long position while also earning returns without risking the funds in a market trade.
One of the top-performing tokens in the market is the DAPP token, which is the native token of LiquidApps (DAPP Network). The DAPP token has a total supply of 1,000,000,000 DAPPs, its token generation has started since Feb 26, 2019, and it will end on Jan 25, 2020.
One of the key facts that make DAPP token a top-performing staking token is the fact that investors staking the DAPP token can expect a nice return of about 9% annually.
For long-term crypto hodlers, staking the DAPP token for a decent 9% annual return is a nice low-risk use case compared to low-risk traditional and crypto investments. For instance, people who stake on NEO can only expect a 5.5% annual return on their portfolio.
The best part is that staking DAPP token is a simple process that involves navigating to the “dappservices” account, selecting the “selectpkg” action, and filling in the required information.
Afterward, you’ll need to execute a “stake” command and you can expect to start earning interest based on the number of tokens you are staking.
When you are done staking, you’ll execute the “unstake” command and input the same parameters you provided while staking.
Staking is a win-win whether you are trading or holding
Last week Binance, one of the biggest cryptocurrencies by trading volume revealed that it has launched a crypto lending business to enable long-term holders to earn more rewards from maintaining their positions.
Binance Lending functionally allow holders to stake their coins in the market to earn guaranteed rewards irrespective of how the market moves.
Binance Lending will freeze staked amount during the crypto lending period, and it will unfreeze the principal staked and interest accrued on the redemption date of the contract.
Celsius is another crypto startup that is built around the idea that long-term hodler should be able to record additional rewards on their portfolios beyond basic price gains.
With Celsius, holders can earn interest on their cryptocurrency holdings and they can borrow against such positions without paying any fees. Celsius says it has originated about $2.2B in loans disbursed to more than 40,000 wallets.
The rising popularity of staking suggests that long-term hodlers can earn guaranteed low-risk returns on their portfolios.
In addition, traders who want to take a break from the rollercoaster volatility of active trading can still take advantage of staking to profit irrespective of whether cryptocurrencies are trading up, down or sideways.
Disclaimer: This is a contributed article and should not be taken as investment advice
















