Following its Friday launch, the “Internet Computer” (ICP) token has become the 4th-largest cryptocurrency by market cap, according to data from CoinMarketCap.com.
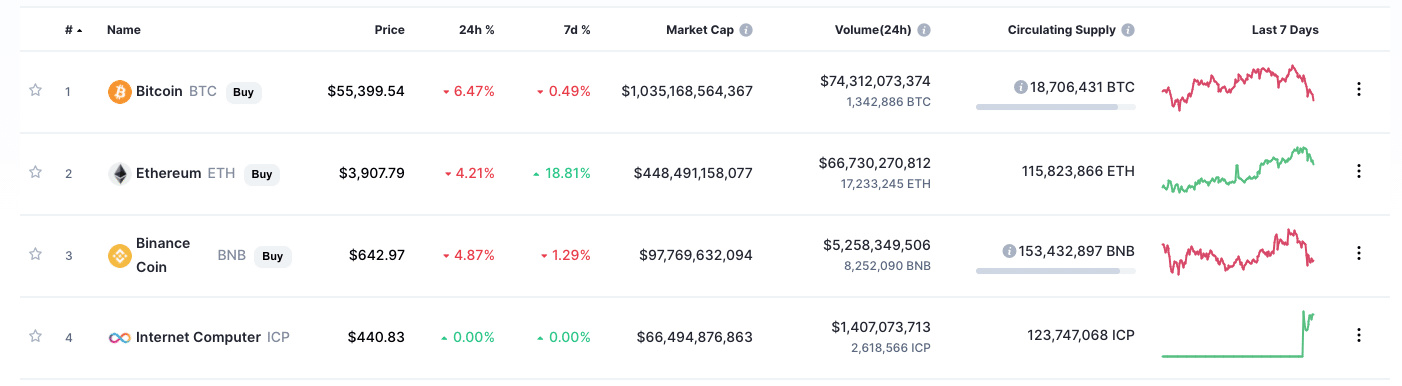
How did this happen? The project’s token, named Internet Computer Price (ICP), has been launching on a number of high-profile cryptocurrency exchanges throughout the course of the last week, including OKEx, Huobi, Binance, Gate.io, Coinbase and others.
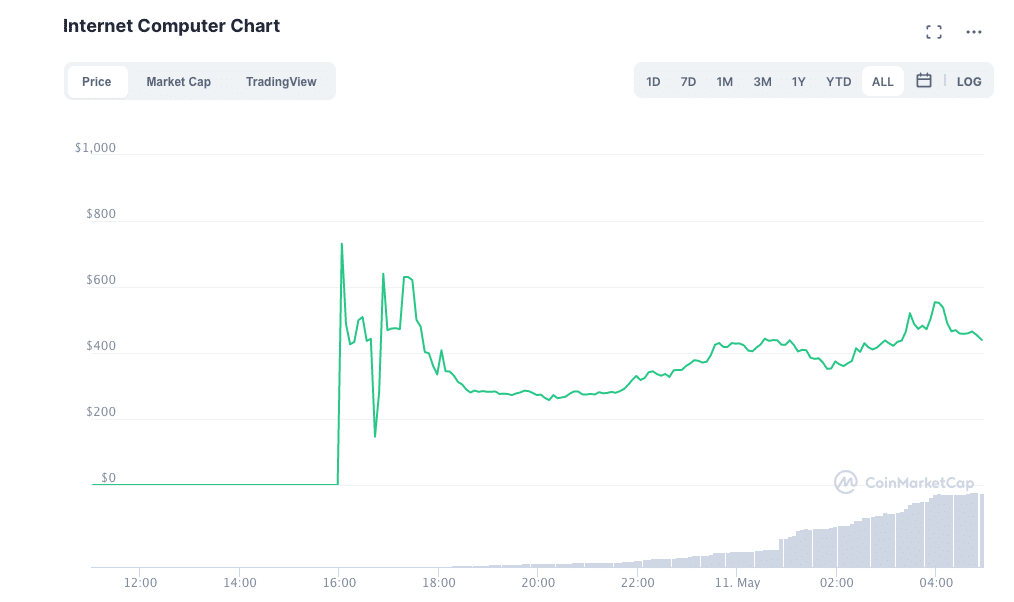
The sudden appearance of the token in such a high place on CoinMarketCap’s official rankings has stunned a number of analysts within the Blockchain community.
However, while the ICP token may have only recently launched, the project has actually been in the works for five years, developed by Zurich-based non-for-profit organization, Dfinity. It has also attracted several impressive backers, including Andreessen-Horowitz and Polychain Capital.
According to CoinDesk, the project launched late last week with “multiple ecosystem companies,” including “Enso Finance (a decentralized exchange), Distrikt (a professional social network), Fleek (infrastructure for the decentralized web) and Origyn (a provenance platform for luxury goods), among several others.”
Some Crypto Community Members Are Skeptical of the Internet Computer
The project’s aims are ambitious. Dominic Williams, the Chief Scientist at Dfinity, reportedly told CoinDesk that: “We want people to abandon traditional IT and move all systems and services to smart contracts.”
Internet Computer Association (ICA)
— Dominic Williams ∞ (@dominic_w) May 11, 2021
- Geneva not-for-profit
- Advocates for Internet Computer
- Coords & supports ecosystem participants
Excited to see what the ICA can do for the ecosystem.https://t.co/wfUJfhfRAE
However, the project is attracting some criticism from crypto community members. Twitter user @GreatGrandBear described the project as “centralized crap + some marketing.” Others have called the project an attempted “Ethereum killer.”
What Is the Internet Computer? A Brief Technical Overview
However, the project is pushing back. Dominic Williams said that the Internet Computer is “not an Ethereum killer.” Other proponents of the network have pointed out that the new blockchain could be used to protect Ethereum.
Help me get this out :)
— Dominic Williams ∞ (@dominic_w) May 9, 2021
* Yes, the Internet Computer IS a blockchain
* It has nothing to do with cloud (but, yes, smart contracts run at web speed, with unlimited capacity)
* Smart contracts will rule the world
* Not an "Ethereum-killer".
* Something new
Tick tock...
The Internet Computer has branded itself as “the last original Layer 1 blockchain project is launching a revolutionary public network that provides a limitless environment for smart contracts that run at web speed, serve web, scale and reduce compute costs by a million times or more.”
According to the project’s website, the Internet Computer aims to “extend the functionality of the public Internet so that it can host backend software, transforming it into a global comput[ing] platform.” The project claims that developers can ditch centralized servers and commercial cloud services, and instead can use the Internet Computer to create websites, internet services, enterprise IT services and more.
@dfinity is focused on building the “Internet Computer”, a blockchain network aiming to expand the functionality of the internet.
— Messari (@MessariCrypto) May 10, 2021
It aims to build a decentralized, scalable cloud-like platform that can store data, perform computation, and support community-driven governance.
The Internet Computer’s “Chain Key Technology”
In addition, the project boasts the creation and usage of Chain Key Technology, which is the method by which transactions are confirmed on the network. According to the project’s website, the technology “allows the Internet Computer to finalize transactions that update smart contract state in 1–2 seconds.”
Moreover, Chain Key Technology allows the internet computer to operate with a single public key, which “allows any device, including smartwatches and mobile phones, to verify the authenticity of artifacts from the Internet Computer.” In other words, the blockchain reportedly has a more scalable method of verifying transactions and digital objects than other blockchains may have.
The most notable innovation of Chain Key Technology is that the #InternetComputer has a single public key, enabling any device to verify the authenticity of artifacts generated by the Internet Computer, even smart watches and mobile phones.
— DFINITY Foundation (@dfinity) May 7, 2021
Watch live: https://t.co/PrfUvyAO9V pic.twitter.com/UsWpWXyFIZ
The project officially went open-source on May 10th, a move that the project says will allow developers “to build the code and verify that it derives to the same binary image that is referenced in upgrade proposals published via the Network Nervous System (NNS).”
On May 10 at 10:00 CEST, @dfinity open sourced the #InternetComputer.
— DFINITY Foundation (@dfinity) May 10, 2021
Now that the #InternetComputer is launched, the source code of 3 primary components is live: replica, nodemanager, and NNS canisters. pic.twitter.com/iMt7T3vRhd
What are your thoughts on the Internet Computer? Let us know in the comments below.






















